-
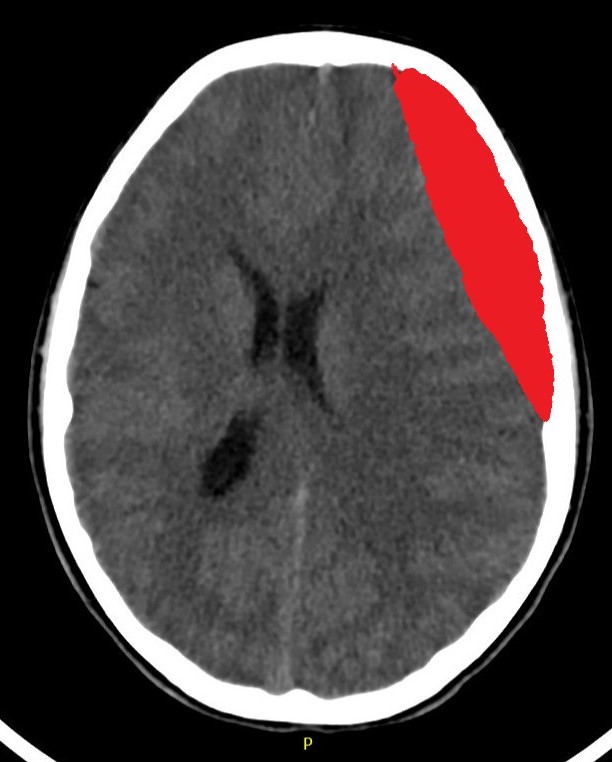
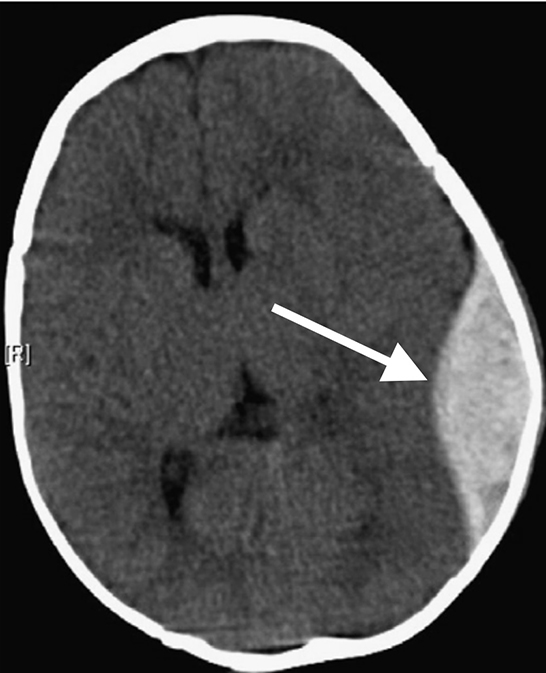
Subdural Hemorrhage
This is a Subdural Hemorrhage (SDH). When blood collects between the outermost membranes surrounding your brain, it takes the shape of a crescent. This often happens when veins that cross this area are torn. This type of bleeding requires close monitoring. If the bleeding continues or the clot grows larger, it may require an operation to remove the blood and relieve the pressure on your brain.
-
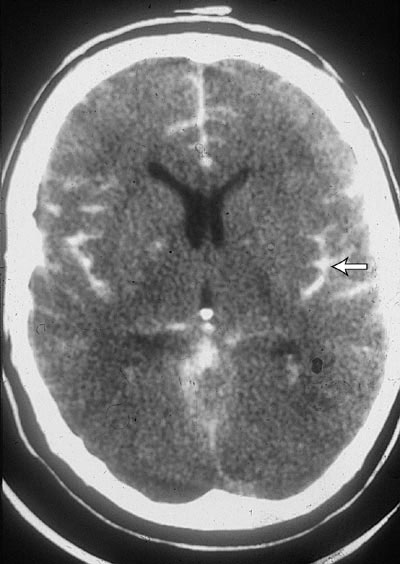
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
This is Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH). When you have a SAH bleed, the bleeding occurs closer to the delicate brain tissue, in the innermost layers covering the brain. These layers are weak, so the bleeding takes an irregular shape around the brain. Because these layers are fragile, and the bleeding occurs deeper in the skull, an operation to remove this blood is not likely to help.
-
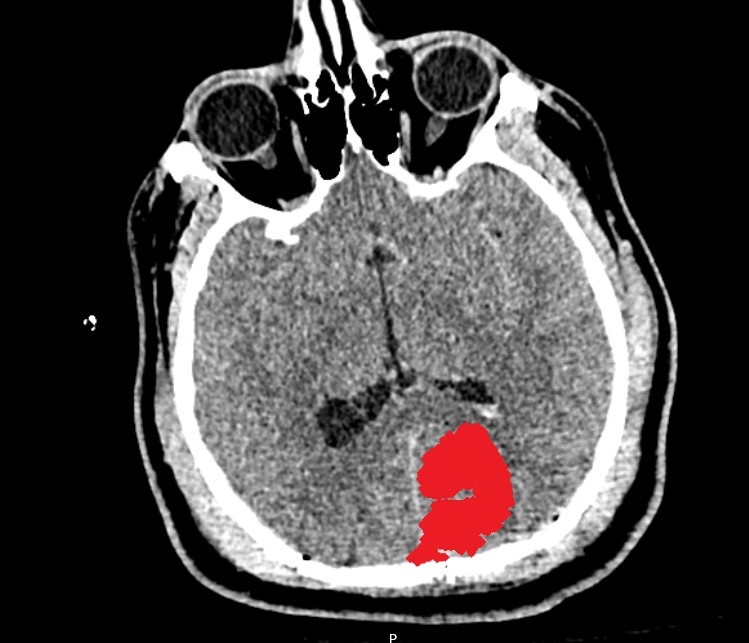
Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage
This is an Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage (IPH). This bleeding occurs inside of your brain. An IPH is a severe injury because there are no layers that separate your brain from that blood that collects within it. On CT, this bleeding will look like a collection of blood. This blood can cause your brain to 'shift' and damage your brain from the inside out. It commonly occurs in more than one area of the brain after a traumatic injury.
-
Epidural Hemorrhage
This is an Epidural Hemorrhage (EDH). This bleeding occurs between your skull and the outermost membrane that protects your brain. Bleeding that occurs between these layers is often described as a "lens" shaped on CT. Arterial bleeding is often the cause of this injury. Depending on the amount of blood, an operation may be required to remove the clot.
-
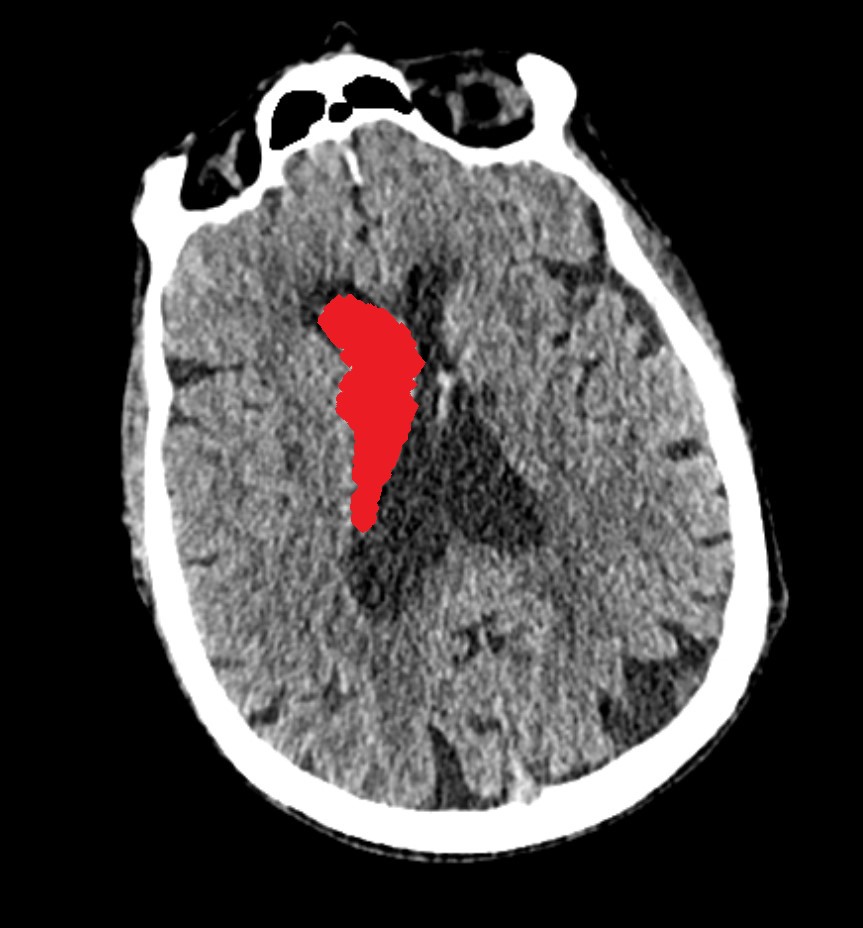
Intraventricular Hemorrhage
This is an Intraventricular Hemorrhage (IVH). The ventricles are spaces in your brain where the protective fluid (called cerebrospinal fluid) is made. Damage to the small arteries around the ventricles is usually the cause of this type of injury. On a CT scan, your doctor may identify blood inside the ventricles. When there is blood in this area, there is often bleeding in other parts of your brain. It may require the placement of an external ventricle drain (called an EVD) to relieve the pressure on your brain.