To share on Twitter click the button below or credit @VI4research!
Sharing elsewhere? Credit this page.
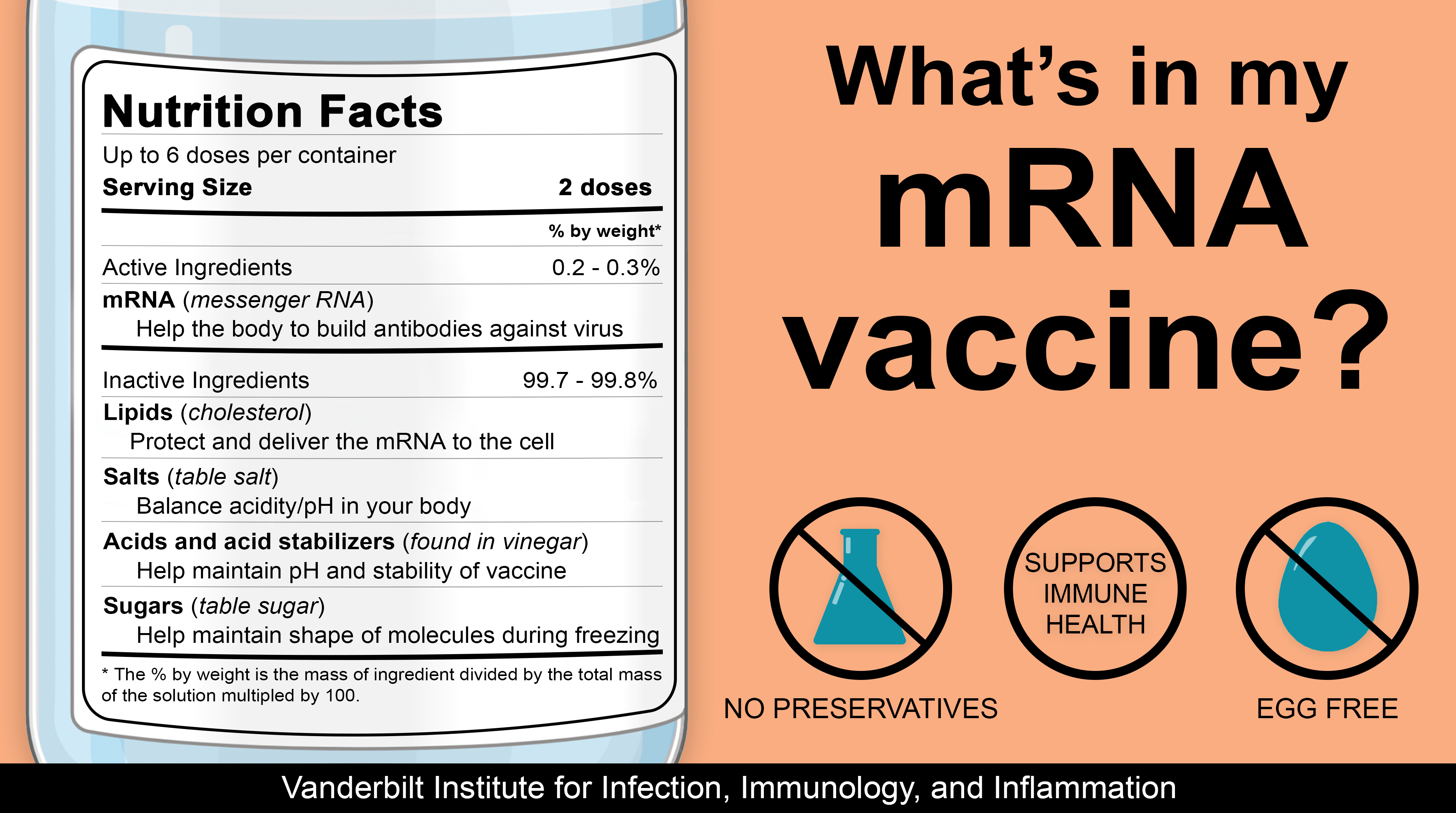
What's in my mRNA Vaccine?
The mRNA vaccine is a new type of vaccine that allows your body to trigger an immune response without using the actual germ to train your immune system. Instead, it trains your immune response using a piece of the virus and will later protect you from getting infected/sick if you encounter the actual virus. Since it is new, here is a list of the generalized ingredients for the mRNA vaccines currently available in the US.
Active Ingredient
There is only one active ingredient in these vaccines, nucleoside-modified messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA). mRNA are genetic instructions that train your body how to make the viral proteins (spike proteins in the case of SARS-CoV-2) that are present on the virus. Since this is a foreign protein, your body responds by building an immune response in the form of antibodies that will later recognize the same spike protein on the live virus. Currently, mRNA makes up 0.2-0.3% of the COVID-19 vaccine, depending on which vaccine you receive.
Inactive Ingredients (99.7-99.8%)
There are four main categories for the inactive ingredients: lipids, salts, acids/acid stabilizers, and sugars. These make up the rest of the vaccine or 99.7-99.8%, depending on the COVID-19 vaccine you receive.
Lipids are molecules that are insoluble in water like oils. They are used in this vaccine to protect and deliver the mRNA to the cell. Examples of some of these lipids in the COVID-19 vaccines include:
- Cholesterol, a common lipid that is found in many foods and your body
- ((4-hydroxybutyl)azanediyl)bis(hexane-6,1-diyl)bis(2-hexyldecanoate), a specialized lipid designed for these vaccines specifically
Salts are molecules soluble in water that balance the acidity and maintain the pH in your body after receiving the vaccine. Examples of some of these salts in the COVID-19 vaccines include:
- Potassium chloride, found in many frozen foods, sports drinks, and baby formula
- Sodium chloride or more commonly known as table salt
Acids/acid stabilizers are hydrogen-containing molecules with a pH less than 7. These are similar to the salts in that they help maintain the pH to that of your body, but these also help stabilize the vaccine to last longer and at lower temperatures for ease in transportation. Here are a few examples of acids/acid stabilizers in the COVID-19 vaccines:
- acetic acid, the main ingredient in vinegar
- tromethamine, currently used as a blood/urine acid reducer by doctors in a hospital or clinic setting and often used after heart bypass surgery or cardiac arrest
Lastly, sugars are the sweet-tasting, water-soluble molecules that specifically contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. These help the other molecules such as mRNA maintain their shapes while frozen/during freezing, allowing the vaccines to last longer. Here is an example of sugars in the COVID-19 vaccines:
- Sucrose or more commonly known as table sugar
Though this is the newest method for vaccination, it has been widely researched in the many years before COVID-19 became a worry. Scientists have been developing mRNA vaccines for years in cancer and infectious diseases like influenza, Zika, and rabies. This vaccine utilizes the development in the lab with readily available materials, which can then easily be standardized and scaled up. This mRNA vaccine technology may allow for one vaccine to then protect against multiple diseases.
A Simple Breakdown of the Ingredients in the COVID Vaccines
Graphics were created using BioRender.