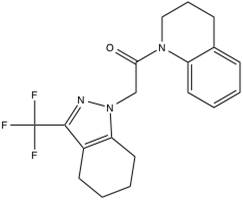
VU590
VU590 was the first publically disclosed small-molecule inhibitor of Kir1.1 (Lewis et al.. Mol Pharm, 2009). It inhibits Kir1.1 with an IC50 of 220 nM and Kir7.1 with an IC50 of 8 uM, but has no apparent effect on Kir2.1 or Kir4.1. VU590 inhibits Kir1.1 and Kir7.1 in the same approximate location of the pore, but does so through unique ligand-channel interfaces (Kharade et al. Mol Pharm, 2017). VU590 can be purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Tocris Biosciences, or Toronto Research Chemicals.
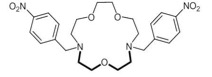
VU591
VU591 was the first publicly disclosed, selective Kir1.1 inhibitor (IC50=240 nM)(Bhave et al., Mol Pharm, 2011). It blocks the pore of Kir1.1 through interactions with Valine 168 and Asparagine 171 (Swale et al., Biophys. J, 2015). VU591 is available from Sigma-Aldrich and Tocris Bioscieces.
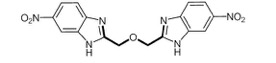
VU573
VU573 is a mixed inhibitor of Kir2.3, Kir3.X, and Kir7.1 (Raphemot et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2011). It also kills mosquitoes by inducing renal failure when injected into the abdomen (Raphemot et al., PLoS One, 2013).
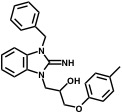
VU063
VU063 was discovered serendipitously in a screen for inhibitors of mosquito Kir1 channels (Raphemot et al., Mol Pharm, 2014). It activates the pancreatic/brain form of KATP channels comprised of Kir6.2 pore-forming subunits and regulatory SUR1 subunits. VU063 is commercially available from EMD/Millipore.
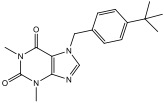
ML418
ML418 was the first selective inhibitor of Kir7.1 (Swale et al., ACS Chem Neurosci, 2016). ML418 inhibits Kir7.1 with an IC50 of 300 nM by blocking the pore of the channel.
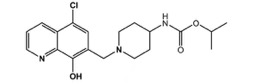
VU625
VU625 was discovered in a high-throughput screen for inhibitors of mosquito Kir1 channels and is currently the most potent inhibitor of Kir1 (IC50=100 nM) known. VU625 is rapidly excreted in the urine and therefore must be co-injected with probenicid to elicit renal failure and death in mosquitoes (Raphemot et al. PLoS, 2014).
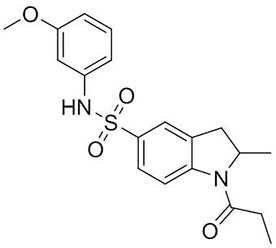
VU041
VU041 is currently the state-of-the-art mosquito Kir1 inhibitor. VU041 inhibits heterologously expressed Kir1 with an IC50 of ~500 nM, inhibits renal function after topical application, and kills insecticide-resistant strains of Aedes aegypti (carriers of Zika virus) and Anopheles gambiae (carriers of Malaria) as effectively as wild type strains of these mosquitoes. VU041 shows proof of concept that inhibition of Kir1 channels can overcome insecticide resistance in mosquitoes (Swale et al., Sci Reports, 2016).