|
|
THE PROBLEM: INFLAMMATORY AND AUTOINFLAMMATORY DISEASES HAVE HIGH MORBIDITY, LIMITED DIAGNOSTIC SPECIFICITY AND SUBOPTIMAL TREATMENT.THE HYPOTHESIS: INTRACELLULAR AND EXTRACELLULAR NON-CODING RNAs CONSTRUCTIVELY REGULATE INFLAMMATORY PROGRAMS, AND CAN BE LEVERAGED TO BOTH UNCOVER AND CONTROL NOVEL MOLECULAR NETWORKS IN DISEASE.THE MISSION: TO USE THE STUDY OF RNA IN IMMUNOLOGY TO DISCOVER NOVEL MECHANISMS AND THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES FOR PATHOLOGIC TISSUE INFLAMMATION. |
miRNA in Immune Effector Cells |
Extracellular RNA Communication |
|
|
|
|
|
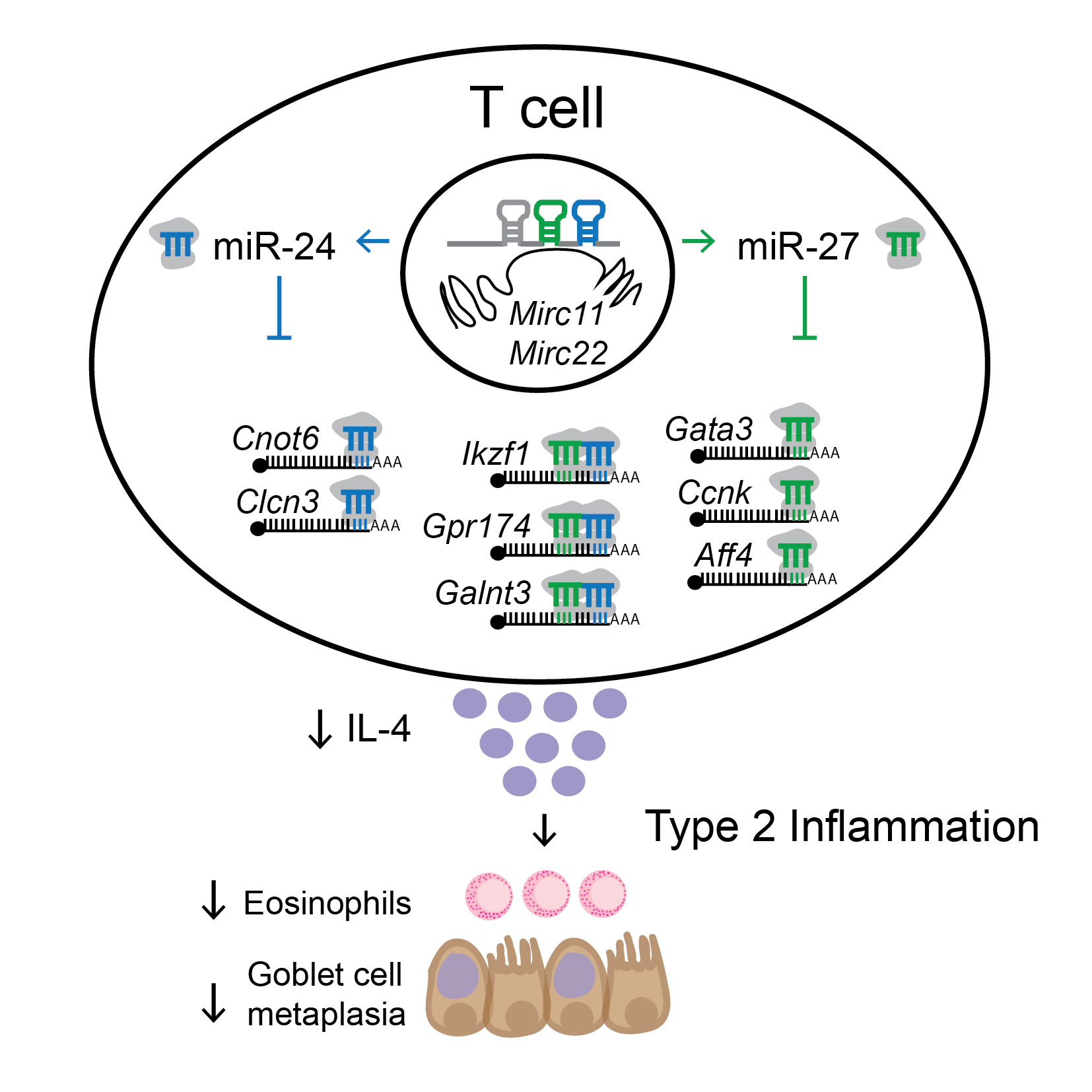
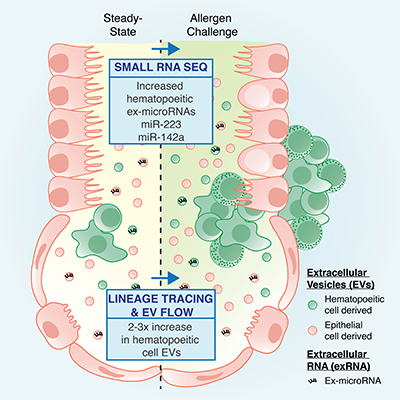
| MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression. They have the ability to alter immune cell function, modify immune responses and impact pathologic tissue inflammation. In previous work (Pua et al. 2016), we have identified that miR-24 and miR-27 collaborate to limit the Th2 cell differentiation and function which drives allergic-type inflammatory responses in the lung. We also identified a network of known and novel genes as essential downstream targets of these miRNAs. | Small non-coding RNAs are both stable and enriched in the extracellular space, including biofluids. They have been proposed to provide a novel form of cell-to-cell communication. In previous work (Pua et al. 2019), we have found that immune-cell associated miRNAs are upregulated in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in a mouse model of asthma. Additionally, we have used a genetic membrane tracing system with vesicle flow cytometry to determine immune extracellular vesicles are also increased during this allergic inflammatory response in the lung. | |
|
QUESTIONS:
|
QUESTIONS:
|